注意
点击此处下载完整示例代码
音频重采样¶
作者: Caroline Chen, Moto Hira
本教程展示了如何使用 torchaudio 的重采样 API。
import torch
import torchaudio
import torchaudio.functional as F
import torchaudio.transforms as T
print(torch.__version__)
print(torchaudio.__version__)
2.7.0
2.7.0
准备工作¶
首先,我们导入模块并定义辅助函数。
import math
import timeit
import librosa
import matplotlib.colors as mcolors
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import pandas as pd
import resampy
from IPython.display import Audio
pd.set_option("display.max_rows", None)
pd.set_option("display.max_columns", None)
DEFAULT_OFFSET = 201
def _get_log_freq(sample_rate, max_sweep_rate, offset):
"""Get freqs evenly spaced out in log-scale, between [0, max_sweep_rate // 2]
offset is used to avoid negative infinity `log(offset + x)`.
"""
start, stop = math.log(offset), math.log(offset + max_sweep_rate // 2)
return torch.exp(torch.linspace(start, stop, sample_rate, dtype=torch.double)) - offset
def _get_inverse_log_freq(freq, sample_rate, offset):
"""Find the time where the given frequency is given by _get_log_freq"""
half = sample_rate // 2
return sample_rate * (math.log(1 + freq / offset) / math.log(1 + half / offset))
def _get_freq_ticks(sample_rate, offset, f_max):
# Given the original sample rate used for generating the sweep,
# find the x-axis value where the log-scale major frequency values fall in
times, freq = [], []
for exp in range(2, 5):
for v in range(1, 10):
f = v * 10**exp
if f < sample_rate // 2:
t = _get_inverse_log_freq(f, sample_rate, offset) / sample_rate
times.append(t)
freq.append(f)
t_max = _get_inverse_log_freq(f_max, sample_rate, offset) / sample_rate
times.append(t_max)
freq.append(f_max)
return times, freq
def get_sine_sweep(sample_rate, offset=DEFAULT_OFFSET):
max_sweep_rate = sample_rate
freq = _get_log_freq(sample_rate, max_sweep_rate, offset)
delta = 2 * math.pi * freq / sample_rate
cummulative = torch.cumsum(delta, dim=0)
signal = torch.sin(cummulative).unsqueeze(dim=0)
return signal
def plot_sweep(
waveform,
sample_rate,
title,
max_sweep_rate=48000,
offset=DEFAULT_OFFSET,
):
x_ticks = [100, 500, 1000, 5000, 10000, 20000, max_sweep_rate // 2]
y_ticks = [1000, 5000, 10000, 20000, sample_rate // 2]
time, freq = _get_freq_ticks(max_sweep_rate, offset, sample_rate // 2)
freq_x = [f if f in x_ticks and f <= max_sweep_rate // 2 else None for f in freq]
freq_y = [f for f in freq if f in y_ticks and 1000 <= f <= sample_rate // 2]
figure, axis = plt.subplots(1, 1)
_, _, _, cax = axis.specgram(waveform[0].numpy(), Fs=sample_rate)
plt.xticks(time, freq_x)
plt.yticks(freq_y, freq_y)
axis.set_xlabel("Original Signal Frequency (Hz, log scale)")
axis.set_ylabel("Waveform Frequency (Hz)")
axis.xaxis.grid(True, alpha=0.67)
axis.yaxis.grid(True, alpha=0.67)
figure.suptitle(f"{title} (sample rate: {sample_rate} Hz)")
plt.colorbar(cax)
重采样概述¶
要将音频波形从一个频率重采样到另一个频率,可以使用 torchaudio.transforms.Resample 或 torchaudio.functional.resample()。transforms.Resample 会预先计算并缓存用于重采样的核,而 functional.resample 会实时计算,因此在使用相同参数对多个波形进行重采样时,使用 torchaudio.transforms.Resample 会带来速度提升(参见性能基准测试部分)。
这两种重采样方法都使用带限 sinc 插值来计算任意时间步长的信号值。实现涉及卷积,因此我们可以利用 GPU / 多线程来提升性能。
注意
在多个子进程中使用重采样时(例如使用多个工作进程加载数据),您的应用程序可能会创建比系统能高效处理的线程更多的线程。在这种情况下,设置 torch.set_num_threads(1) 可能会有所帮助。
由于有限数量的样本只能表示有限数量的频率,重采样无法产生完美的结果,并且可以使用各种参数来控制其质量和计算速度。我们通过对对数正弦扫描进行重采样来展示这些特性,对数正弦扫描是一种频率随时间呈指数增长的正弦波。
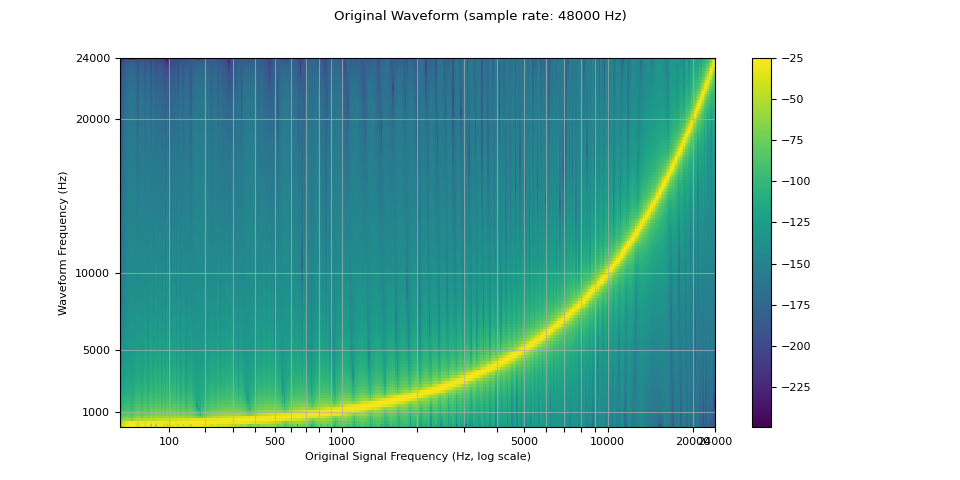
下面的频谱图显示了信号的频率表示,其中 x 轴对应于原始波形的频率(对数刻度),y 轴对应于绘制波形的频率,颜色强度对应于幅度。
sample_rate = 48000
waveform = get_sine_sweep(sample_rate)
plot_sweep(waveform, sample_rate, title="Original Waveform")
Audio(waveform.numpy()[0], rate=sample_rate)
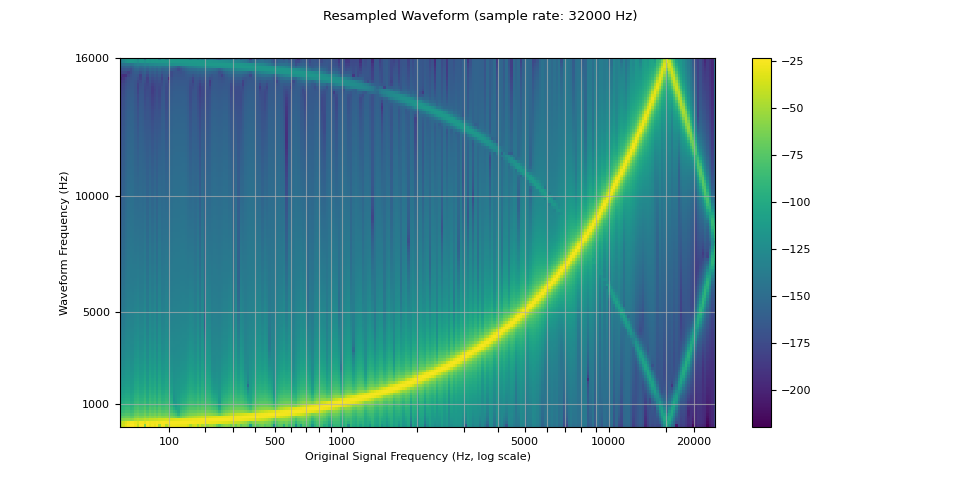
现在我们对其进行重采样(下采样)。
我们看到,在重采样波形的频谱图中,存在一个原始波形中没有出现的伪影。这种效应称为混叠。本页解释了它是如何发生的,以及为什么它看起来像一个反射。
resample_rate = 32000
resampler = T.Resample(sample_rate, resample_rate, dtype=waveform.dtype)
resampled_waveform = resampler(waveform)
plot_sweep(resampled_waveform, resample_rate, title="Resampled Waveform")
Audio(resampled_waveform.numpy()[0], rate=resample_rate)
使用参数控制重采样质量¶
低通滤波器宽度¶
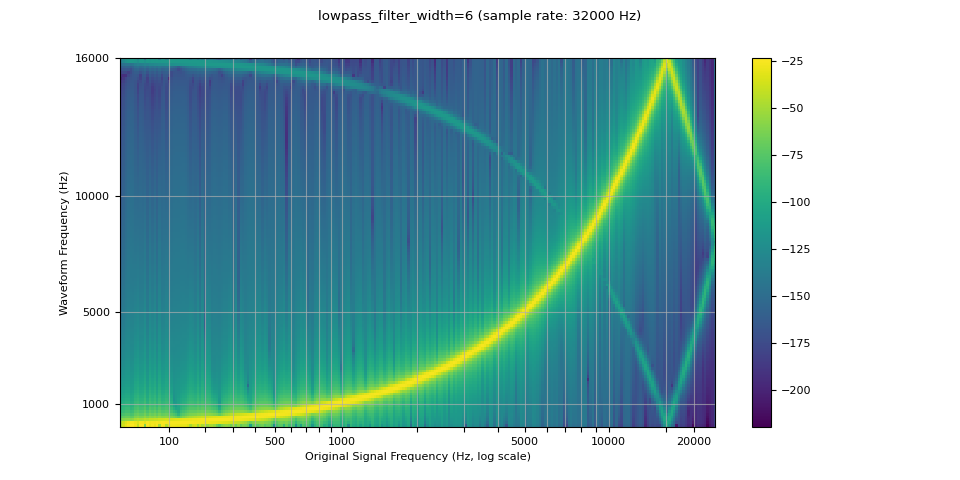
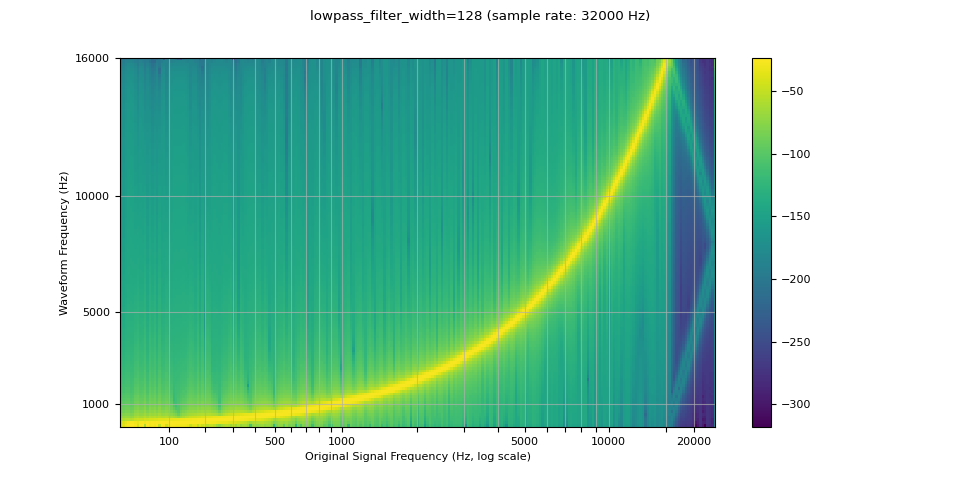
由于用于插值的滤波器无限延伸,因此使用 lowpass_filter_width 参数来控制用于对插值进行窗口化的滤波器宽度。它也称为零交叉点数,因为插值在每个时间单位都穿过零。使用更大的 lowpass_filter_width 可以提供更尖锐、更精确的滤波器,但计算成本更高。
sample_rate = 48000
resample_rate = 32000
resampled_waveform = F.resample(waveform, sample_rate, resample_rate, lowpass_filter_width=6)
plot_sweep(resampled_waveform, resample_rate, title="lowpass_filter_width=6")
resampled_waveform = F.resample(waveform, sample_rate, resample_rate, lowpass_filter_width=128)
plot_sweep(resampled_waveform, resample_rate, title="lowpass_filter_width=128")
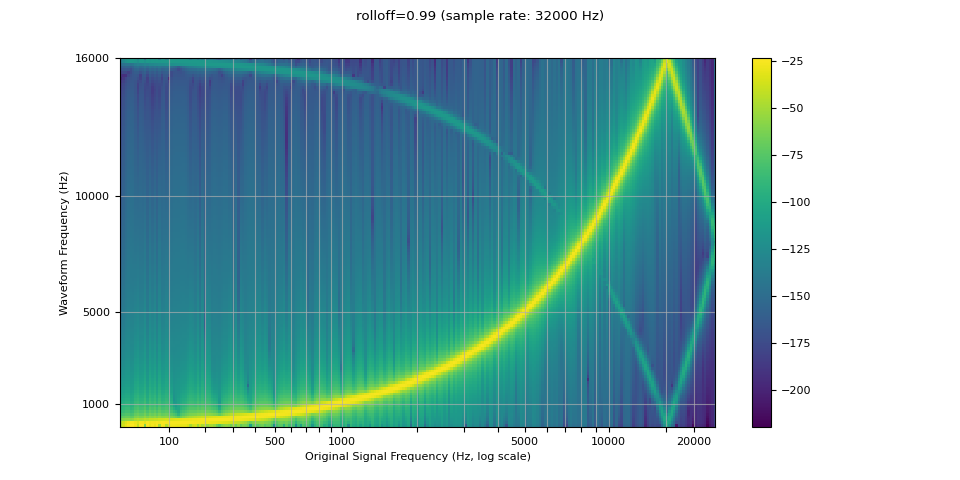
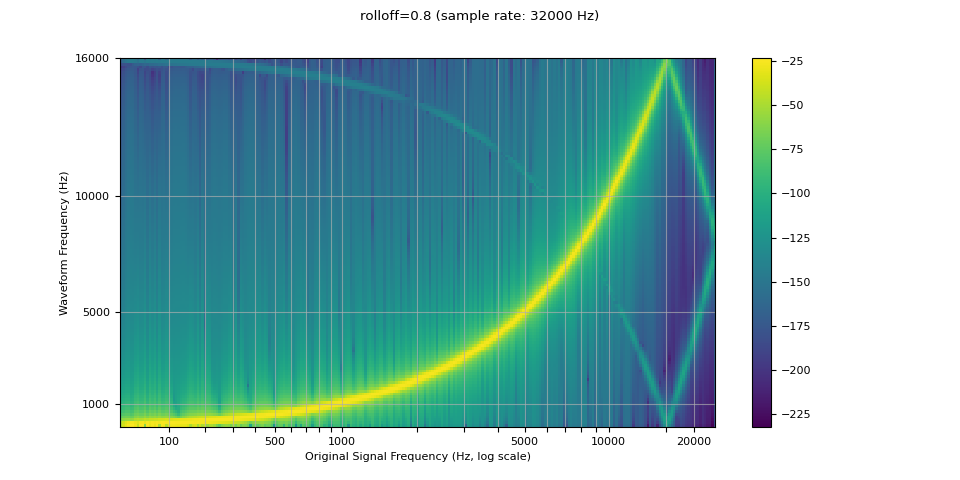
滚降¶
rolloff 参数表示为奈奎斯特频率的一部分,奈奎斯特频率是给定有限采样率可表示的最大频率。rolloff 决定了低通滤波器截止频率,并控制混叠程度,混叠发生在高于奈奎斯特频率的频率被映射到较低频率时。因此,较低的滚降会减少混叠量,但也会降低一些较高频率。
sample_rate = 48000
resample_rate = 32000
resampled_waveform = F.resample(waveform, sample_rate, resample_rate, rolloff=0.99)
plot_sweep(resampled_waveform, resample_rate, title="rolloff=0.99")
resampled_waveform = F.resample(waveform, sample_rate, resample_rate, rolloff=0.8)
plot_sweep(resampled_waveform, resample_rate, title="rolloff=0.8")
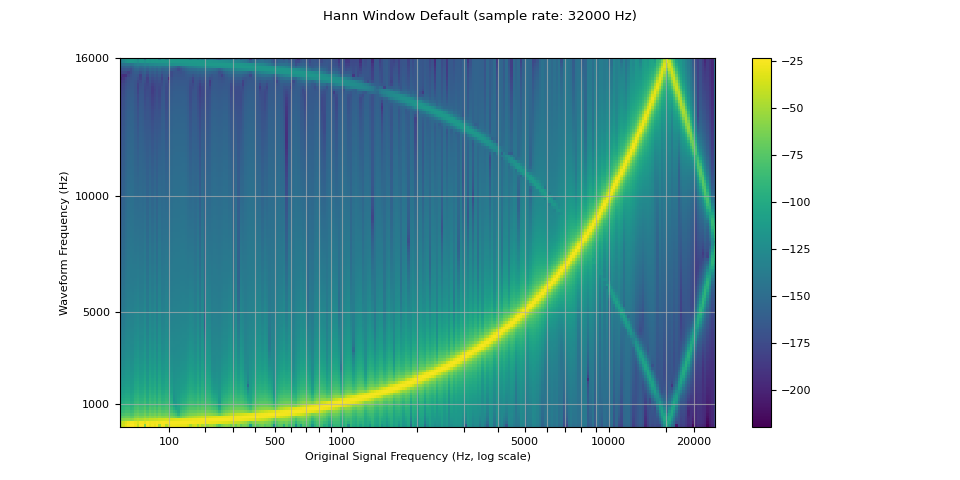
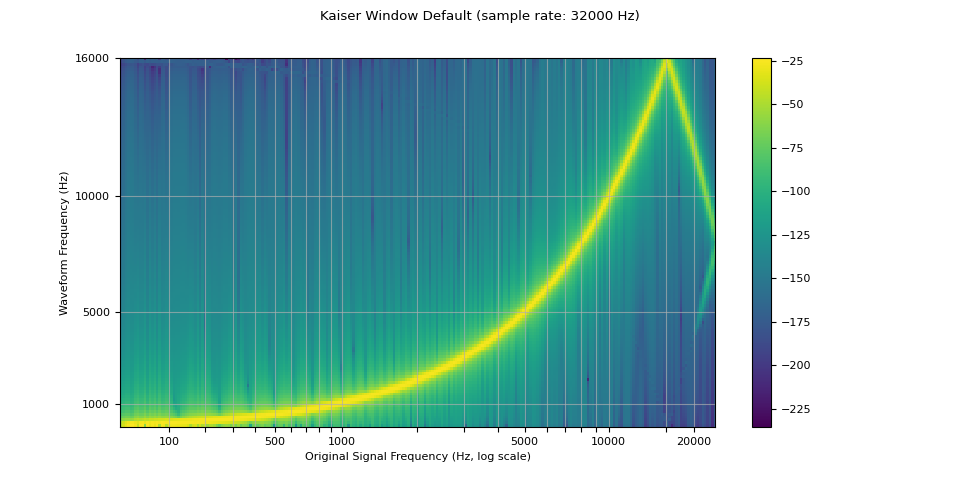
窗函数¶
默认情况下,torchaudio 的重采样使用 Hann 窗滤波器,它是一个加权余弦函数。它还支持 Kaiser 窗,这是一种接近最优的窗函数,包含一个额外的 beta 参数,允许设计滤波器的平滑度和脉冲宽度。这可以使用 resampling_method 参数来控制。
sample_rate = 48000
resample_rate = 32000
resampled_waveform = F.resample(waveform, sample_rate, resample_rate, resampling_method="sinc_interp_hann")
plot_sweep(resampled_waveform, resample_rate, title="Hann Window Default")
resampled_waveform = F.resample(waveform, sample_rate, resample_rate, resampling_method="sinc_interp_kaiser")
plot_sweep(resampled_waveform, resample_rate, title="Kaiser Window Default")
与 librosa 的比较¶
torchaudio 的重采样函数可以产生与 librosa (resampy) 的 kaiser 窗重采样类似的结果,但带有一定噪声
sample_rate = 48000
resample_rate = 32000
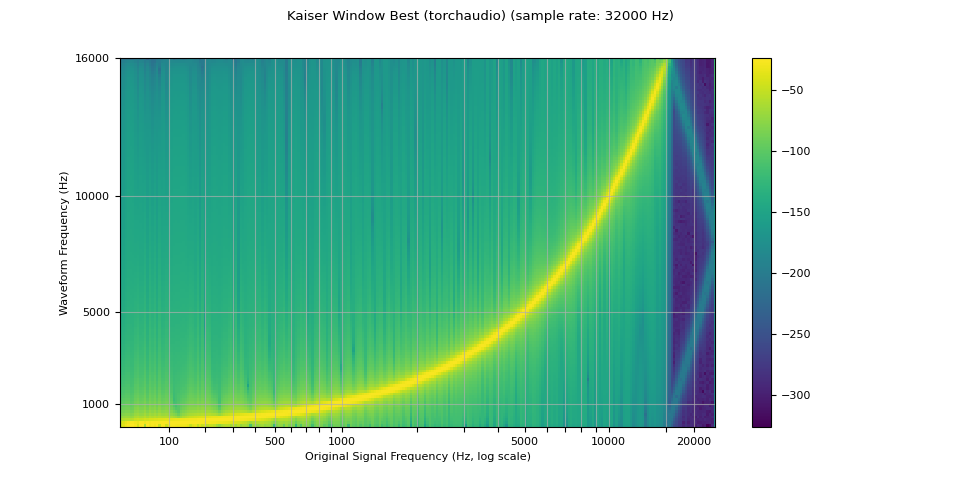
kaiser_best¶
resampled_waveform = F.resample(
waveform,
sample_rate,
resample_rate,
lowpass_filter_width=64,
rolloff=0.9475937167399596,
resampling_method="sinc_interp_kaiser",
beta=14.769656459379492,
)
plot_sweep(resampled_waveform, resample_rate, title="Kaiser Window Best (torchaudio)")
librosa_resampled_waveform = torch.from_numpy(
librosa.resample(waveform.squeeze().numpy(), orig_sr=sample_rate, target_sr=resample_rate, res_type="kaiser_best")
).unsqueeze(0)
plot_sweep(librosa_resampled_waveform, resample_rate, title="Kaiser Window Best (librosa)")
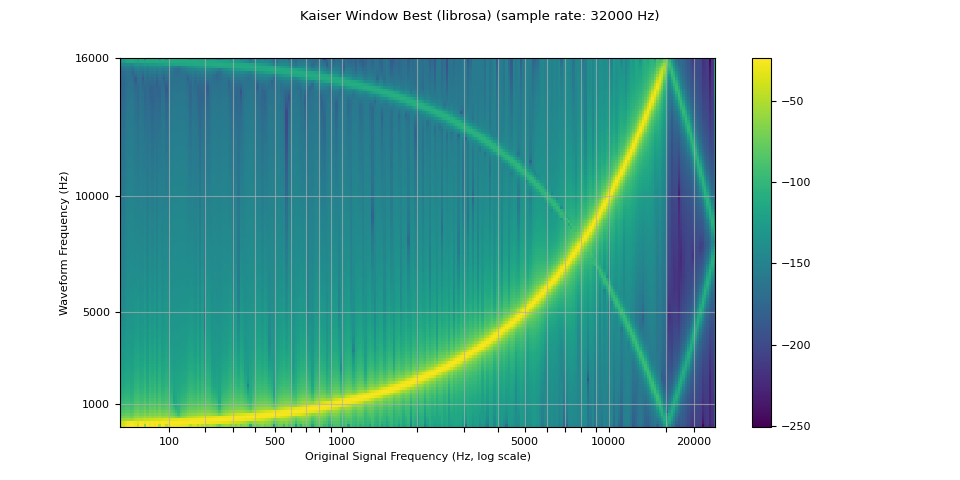
mse = torch.square(resampled_waveform - librosa_resampled_waveform).mean().item()
print("torchaudio and librosa kaiser best MSE:", mse)
torchaudio and librosa kaiser best MSE: 2.0806901153660115e-06
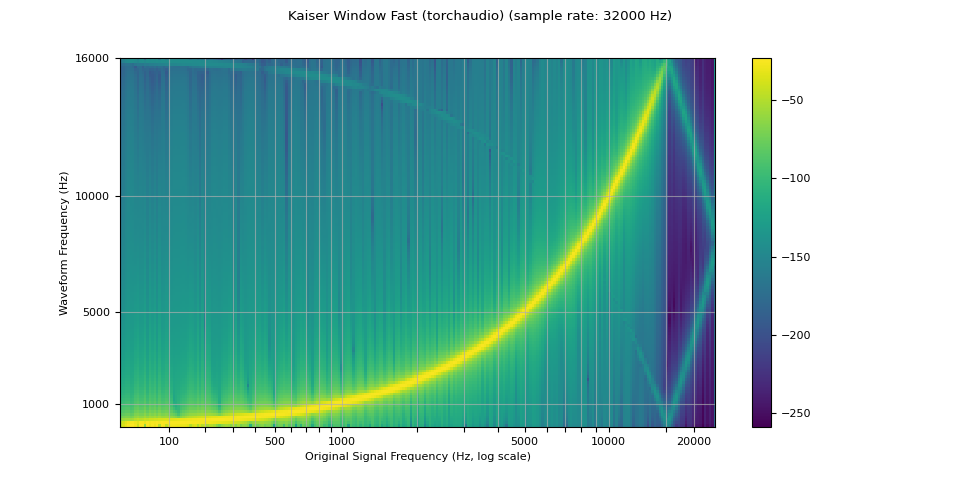
kaiser_fast¶
resampled_waveform = F.resample(
waveform,
sample_rate,
resample_rate,
lowpass_filter_width=16,
rolloff=0.85,
resampling_method="sinc_interp_kaiser",
beta=8.555504641634386,
)
plot_sweep(resampled_waveform, resample_rate, title="Kaiser Window Fast (torchaudio)")
librosa_resampled_waveform = torch.from_numpy(
librosa.resample(waveform.squeeze().numpy(), orig_sr=sample_rate, target_sr=resample_rate, res_type="kaiser_fast")
).unsqueeze(0)
plot_sweep(librosa_resampled_waveform, resample_rate, title="Kaiser Window Fast (librosa)")
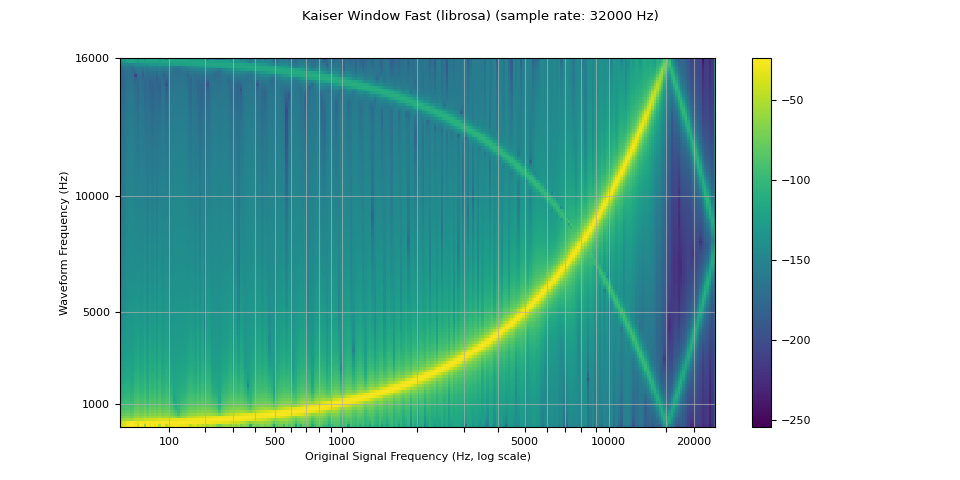
mse = torch.square(resampled_waveform - librosa_resampled_waveform).mean().item()
print("torchaudio and librosa kaiser fast MSE:", mse)
torchaudio and librosa kaiser fast MSE: 2.5200744248601437e-05
性能基准测试¶
以下是两个采样率对之间波形下采样和上采样的基准测试。我们展示了 lowpass_filter_width、窗函数类型和采样率可能带来的性能影响。此外,我们还提供了与 librosa 的 kaiser_best 和 kaiser_fast 在 torchaudio 中使用其对应参数的比较。
print(f"torchaudio: {torchaudio.__version__}")
print(f"librosa: {librosa.__version__}")
print(f"resampy: {resampy.__version__}")
torchaudio: 2.7.0
librosa: 0.10.0
resampy: 0.2.2
def benchmark_resample_functional(
waveform,
sample_rate,
resample_rate,
lowpass_filter_width=6,
rolloff=0.99,
resampling_method="sinc_interp_hann",
beta=None,
iters=5,
):
return (
timeit.timeit(
stmt="""
torchaudio.functional.resample(
waveform,
sample_rate,
resample_rate,
lowpass_filter_width=lowpass_filter_width,
rolloff=rolloff,
resampling_method=resampling_method,
beta=beta,
)
""",
setup="import torchaudio",
number=iters,
globals=locals(),
)
* 1000
/ iters
)
def benchmark_resample_transforms(
waveform,
sample_rate,
resample_rate,
lowpass_filter_width=6,
rolloff=0.99,
resampling_method="sinc_interp_hann",
beta=None,
iters=5,
):
return (
timeit.timeit(
stmt="resampler(waveform)",
setup="""
import torchaudio
resampler = torchaudio.transforms.Resample(
sample_rate,
resample_rate,
lowpass_filter_width=lowpass_filter_width,
rolloff=rolloff,
resampling_method=resampling_method,
dtype=waveform.dtype,
beta=beta,
)
resampler.to(waveform.device)
""",
number=iters,
globals=locals(),
)
* 1000
/ iters
)
def benchmark_resample_librosa(
waveform,
sample_rate,
resample_rate,
res_type=None,
iters=5,
):
waveform_np = waveform.squeeze().numpy()
return (
timeit.timeit(
stmt="""
librosa.resample(
waveform_np,
orig_sr=sample_rate,
target_sr=resample_rate,
res_type=res_type,
)
""",
setup="import librosa",
number=iters,
globals=locals(),
)
* 1000
/ iters
)
def benchmark(sample_rate, resample_rate):
times, rows = [], []
waveform = get_sine_sweep(sample_rate).to(torch.float32)
args = (waveform, sample_rate, resample_rate)
# sinc 64 zero-crossings
f_time = benchmark_resample_functional(*args, lowpass_filter_width=64)
t_time = benchmark_resample_transforms(*args, lowpass_filter_width=64)
times.append([None, f_time, t_time])
rows.append("sinc (width 64)")
# sinc 6 zero-crossings
f_time = benchmark_resample_functional(*args, lowpass_filter_width=16)
t_time = benchmark_resample_transforms(*args, lowpass_filter_width=16)
times.append([None, f_time, t_time])
rows.append("sinc (width 16)")
# kaiser best
kwargs = {
"lowpass_filter_width": 64,
"rolloff": 0.9475937167399596,
"resampling_method": "sinc_interp_kaiser",
"beta": 14.769656459379492,
}
lib_time = benchmark_resample_librosa(*args, res_type="kaiser_best")
f_time = benchmark_resample_functional(*args, **kwargs)
t_time = benchmark_resample_transforms(*args, **kwargs)
times.append([lib_time, f_time, t_time])
rows.append("kaiser_best")
# kaiser fast
kwargs = {
"lowpass_filter_width": 16,
"rolloff": 0.85,
"resampling_method": "sinc_interp_kaiser",
"beta": 8.555504641634386,
}
lib_time = benchmark_resample_librosa(*args, res_type="kaiser_fast")
f_time = benchmark_resample_functional(*args, **kwargs)
t_time = benchmark_resample_transforms(*args, **kwargs)
times.append([lib_time, f_time, t_time])
rows.append("kaiser_fast")
df = pd.DataFrame(times, columns=["librosa", "functional", "transforms"], index=rows)
return df
def plot(df):
print(df.round(2))
ax = df.plot(kind="bar")
plt.ylabel("Time Elapsed [ms]")
plt.xticks(rotation=0, fontsize=10)
for cont, col, color in zip(ax.containers, df.columns, mcolors.TABLEAU_COLORS):
label = ["N/A" if v != v else str(v) for v in df[col].round(2)]
ax.bar_label(cont, labels=label, color=color, fontweight="bold", fontsize="x-small")
下采样 (48 -> 44.1 kHz)¶
df = benchmark(48_000, 44_100)
plot(df)
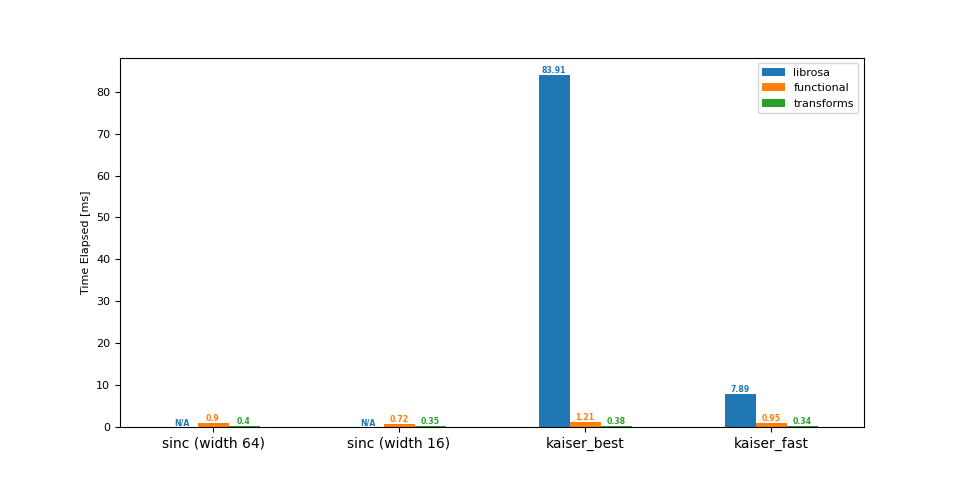
librosa functional transforms
sinc (width 64) NaN 0.90 0.40
sinc (width 16) NaN 0.72 0.35
kaiser_best 83.91 1.21 0.38
kaiser_fast 7.89 0.95 0.34
下采样 (16 -> 8 kHz)¶
df = benchmark(16_000, 8_000)
plot(df)
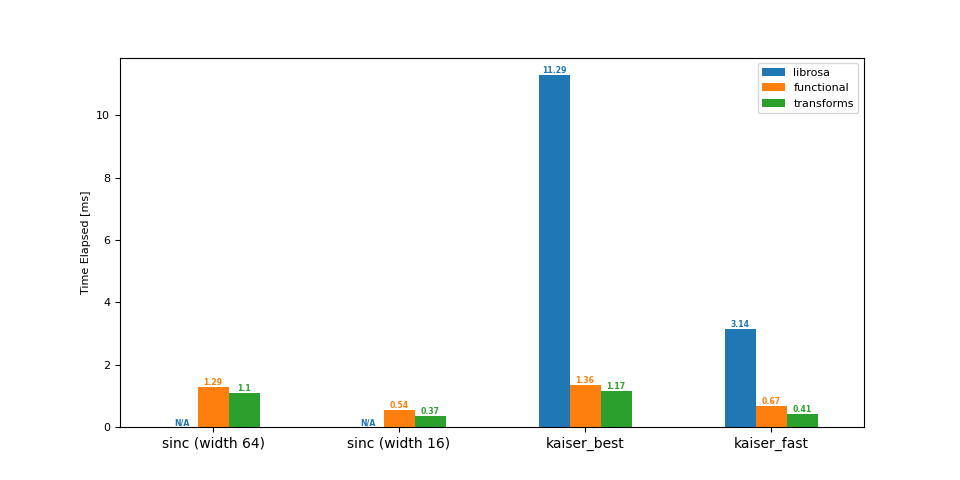
librosa functional transforms
sinc (width 64) NaN 1.29 1.10
sinc (width 16) NaN 0.54 0.37
kaiser_best 11.29 1.36 1.17
kaiser_fast 3.14 0.67 0.41
上采样 (44.1 -> 48 kHz)¶
df = benchmark(44_100, 48_000)
plot(df)
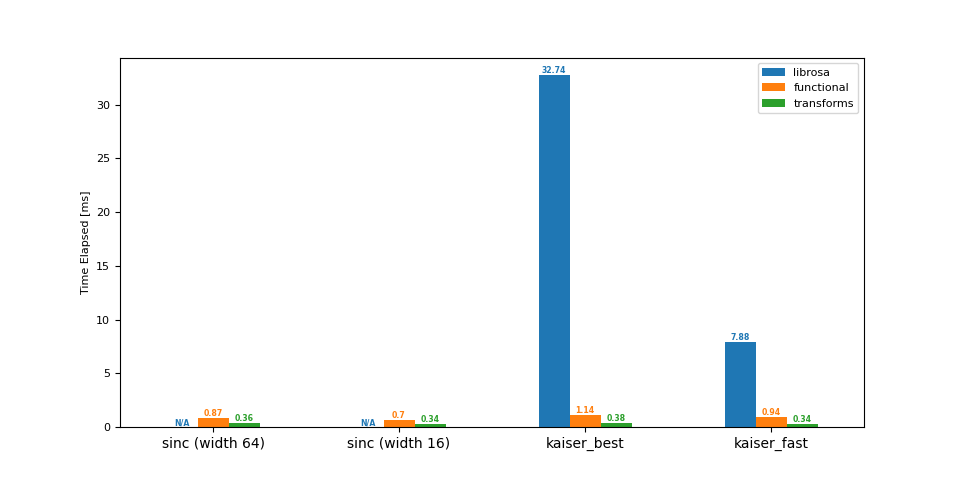
librosa functional transforms
sinc (width 64) NaN 0.87 0.36
sinc (width 16) NaN 0.70 0.34
kaiser_best 32.74 1.14 0.38
kaiser_fast 7.88 0.94 0.34
上采样 (8 -> 16 kHz)¶
df = benchmark(8_000, 16_000)
plot(df)
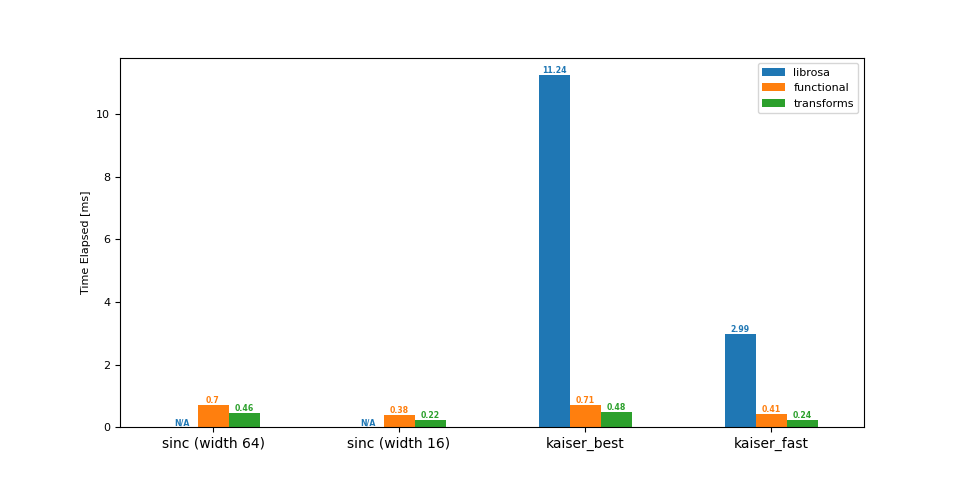
librosa functional transforms
sinc (width 64) NaN 0.70 0.46
sinc (width 16) NaN 0.38 0.22
kaiser_best 11.24 0.71 0.48
kaiser_fast 2.99 0.41 0.24
总结¶
详细阐述结果如下
更大的
lowpass_filter_width会导致更大的重采样核,因此增加了核计算和卷积的计算时间使用
sinc_interp_kaiser比默认的sinc_interp_hann产生更长的计算时间,因为它计算中间窗值更复杂采样率和重采样率之间较大的最大公约数 (GCD) 会导致简化,从而允许使用更小的核和更快的核计算。
脚本总运行时间:( 0 分钟 3.361 秒)



