如何进行分布式数据并行 (DDP)¶
本文档展示了如何在 xla 中使用 torch.nn.parallel.DistributedDataParallel,并进一步描述了它与原生的 xla 数据并行方法的区别。您可以在此处找到一个最小的可运行示例。
背景 / 动机¶
用户长期以来一直要求能够在 xla 中使用 PyTorch 的 DistributedDataParallel API。在此,我们将其作为一个实验性功能启用。
如何使用 DistributedDataParallel¶
对于从 PyTorch eager mode 切换到 XLA 的用户,这里列出了将 eager DDP 模型转换为 XLA 模型所需的所有更改。我们假设您已经知道如何在单个 XLA 设备上使用 XLA。
导入 XLA 特定的分布式包
import torch_xla import torch_xla.runtime as xr import torch_xla.distributed.xla_backend
初始化 XLA 进程组,类似于 nccl 和 gloo 等其他进程组。
dist.init_process_group("xla", rank=rank, world_size=world_size)
如果需要,使用 XLA 特定的 API 来获取 rank 和 world_size。
new_rank = xr.global_ordinal() world_size = xr.world_size()
使用 DDP 封装模型。
ddp_model = DDP(model, gradient_as_bucket_view=True)
最后,使用 XLA 特定的启动器启动您的模型。
torch_xla.launch(demo_fn)
我们将所有内容整合在一起(该示例实际上取自 DDP 教程)。编码方式与 eager 体验非常相似。只是在单个设备上增加了一些 XLA 特定的处理,再加上对您的脚本进行的上述五项更改。
import os
import sys
import tempfile
import torch
import torch.distributed as dist
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.optim as optim
from torch.nn.parallel import DistributedDataParallel as DDP
# additional imports for xla
import torch_xla
import torch_xla.core.xla_model as xm
import torch_xla.runtime as xr
import torch_xla.distributed.xla_backend
def setup(rank, world_size):
os.environ['PJRT_DEVICE'] = 'TPU'
# initialize the xla process group
dist.init_process_group("xla", rank=rank, world_size=world_size)
def cleanup():
dist.destroy_process_group()
class ToyModel(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(ToyModel, self).__init__()
self.net1 = nn.Linear(10, 1000000)
self.relu = nn.ReLU()
self.net2 = nn.Linear(1000000, 5)
def forward(self, x):
return self.net2(self.relu(self.net1(x)))
def demo_basic(rank):
# xla specific APIs to get rank, world_size.
new_rank = xr.global_ordinal()
assert new_rank == rank
world_size = xr.world_size()
print(f"Running basic DDP example on rank {rank}.")
setup(rank, world_size)
# create model and move it to XLA device
device = xm.xla_device()
model = ToyModel().to(device)
ddp_model = DDP(model, gradient_as_bucket_view=True)
loss_fn = nn.MSELoss()
optimizer = optim.SGD(ddp_model.parameters(), lr=0.001)
optimizer.zero_grad()
outputs = ddp_model(torch.randn(20, 10).to(device))
labels = torch.randn(20, 5).to(device)
loss_fn(outputs, labels).backward()
optimizer.step()
# xla specific API to execute the graph
xm.mark_step()
cleanup()
def run_demo(demo_fn):
# xla specific launcher
torch_xla.launch(demo_fn)
if __name__ == "__main__":
run_demo(demo_basic)
性能测试¶
使用假数据的 Resnet50¶
以下结果是在 TPU VM V3-8 环境下使用 ToT PyTorch 和 PyTorch/XLA 通过命令收集的
python test/test_train_mp_imagenet.py --fake_data --model=resnet50 --num_epochs=1
统计指标是使用此拉取请求中的脚本生成的。速率的单位是每秒图像数。
| 类型 | 平均值 | 中位数 | 第 90 百分位 | 标准差 | CV |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| xm.optimizer_step | 418.54 | 419.22 | 430.40 | 9.76 | 0.02 |
| DDP | 395.97 | 395.54 | 407.13 | 7.60 | 0.02 |
我们原生的分布式数据并行方法与 DistributedDataParallel 封装器之间的性能差异是:1 - 395.97 / 418.54 = 5.39%。考虑到 DDP 封装器在跟踪 DDP 运行时时引入了额外的开销,这个结果似乎是合理的。
使用假数据的 MNIST¶
以下结果是在 TPU VM V3-8 环境下使用 ToT PyTorch 和 PyTorch/XLA,通过命令 python test/test_train_mp_mnist.py --fake_data 收集的。统计指标是使用此拉取请求中的脚本生成的。速率的单位是每秒图像数。
| 类型 | 平均值 | 中位数 | 第 90 百分位 | 标准差 | CV |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| xm.optimizer_step | 17864.19 | 20108.96 | 24351.74 | 5866.83 | 0.33 |
| DDP | 10701.39 | 11770.00 | 14313.78 | 3102.92 | 0.29 |
我们原生的分布式数据并行方法与 DistributedDataParallel 封装器之间的性能差异是:1 - 14313.78 / 24351.74 = 41.22%。由于数据集较小,且前几轮受到数据加载的严重影响,因此我们在此比较第 90 百分位。这种减速幅度很大,但考虑到模型很小,这是可以理解的。额外的 DDP 运行时跟踪开销很难被分摊。
使用真实数据的 MNIST¶
以下结果是在 TPU VM V3-8 环境下使用 ToT PyTorch 和 PyTorch/XLA 通过命令收集的
python test/test_train_mp_mnist.py --logdir mnist/ o.
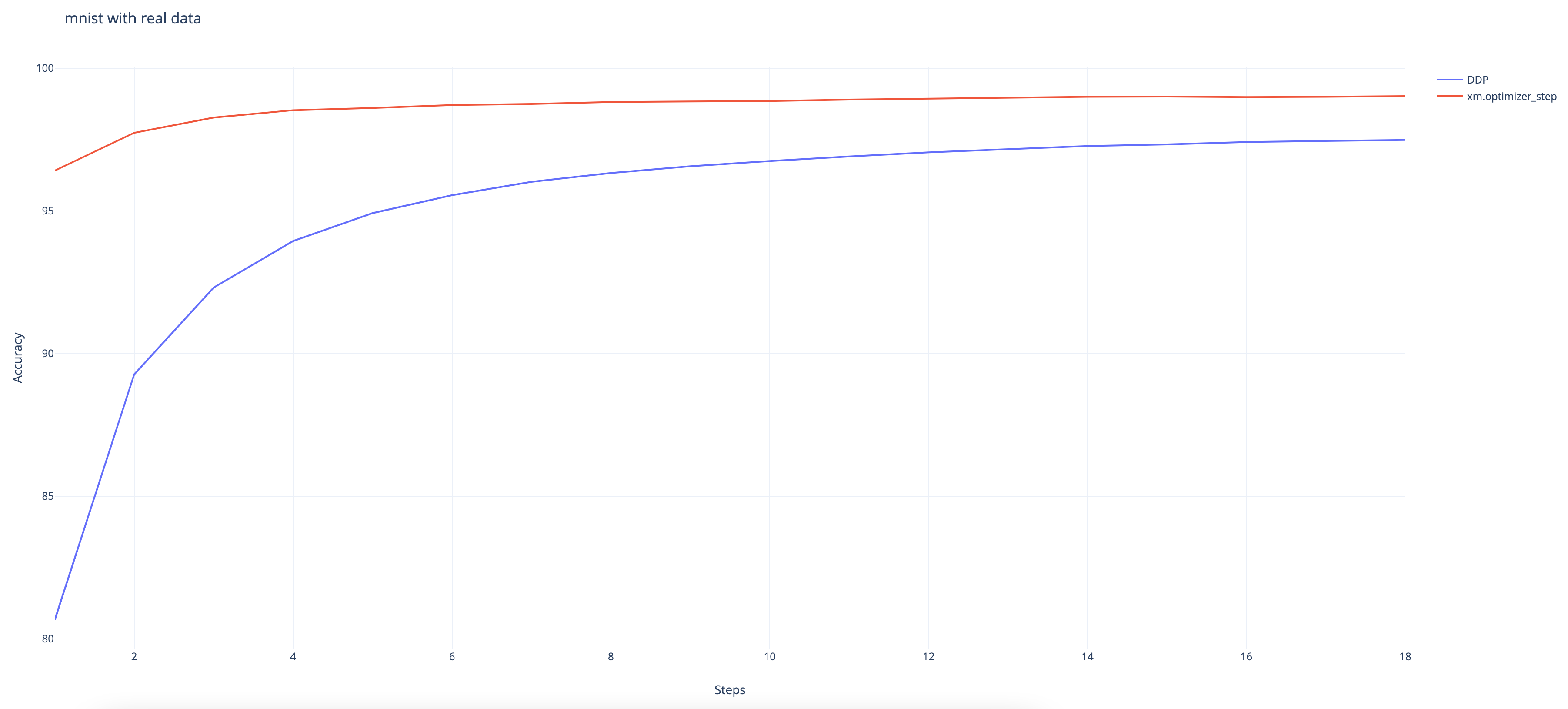
我们可以观察到,即使 DDP 封装器最终仍能达到 97.48% 的高准确率,其收敛速度也比原生的 XLA 方法慢。(原生方法达到了 99%。)
免责声明¶
此功能仍处于实验阶段并正在积极开发中。请谨慎使用,如有任何错误,请随时向 XLA GitHub 仓库提交。对于对原生 XLA 数据并行方法感兴趣的用户,请参阅此处的教程。
以下是一些正在调查中的已知问题:* 与 torch.utils.data.DataLoader 一起使用时存在一些问题。使用真实数据的 test_train_mp_mnist.py 在退出前崩溃。
