ResNeSt
import torch
# get list of models
torch.hub.list('zhanghang1989/ResNeSt', force_reload=True)
# load pretrained models, using ResNeSt-50 as an example
model = torch.hub.load('zhanghang1989/ResNeSt', 'resnest50', pretrained=True)
model.eval()
所有预训练模型都要求输入图像以相同的方式进行归一化,即由形状为 (3 x H x W) 的 3 通道 RGB 图像组成的小批量数据,其中 H 和 W 预计至少为 224。图像必须加载到 [0, 1] 范围内,然后使用 mean = [0.485, 0.456, 0.406] 和 std = [0.229, 0.224, 0.225] 进行归一化。
这是一个示例执行。
# Download an example image from the pytorch website
import urllib
url, filename = ("https://github.com/pytorch/hub/raw/master/images/dog.jpg", "dog.jpg")
try: urllib.URLopener().retrieve(url, filename)
except: urllib.request.urlretrieve(url, filename)
# sample execution (requires torchvision)
from PIL import Image
from torchvision import transforms
input_image = Image.open(filename)
preprocess = transforms.Compose([
transforms.Resize(256),
transforms.CenterCrop(224),
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize(mean=[0.485, 0.456, 0.406], std=[0.229, 0.224, 0.225]),
])
input_tensor = preprocess(input_image)
input_batch = input_tensor.unsqueeze(0) # create a mini-batch as expected by the model
# move the input and model to GPU for speed if available
if torch.cuda.is_available():
input_batch = input_batch.to('cuda')
model.to('cuda')
with torch.no_grad():
output = model(input_batch)
# Tensor of shape 1000, with confidence scores over ImageNet's 1000 classes
print(output[0])
# The output has unnormalized scores. To get probabilities, you can run a softmax on it.
probabilities = torch.nn.functional.softmax(output[0], dim=0)
print(probabilities)
# Download ImageNet labels
!wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/pytorch/hub/master/imagenet_classes.txt
# Read the categories
with open("imagenet_classes.txt", "r") as f:
categories = [s.strip() for s in f.readlines()]
# Show top categories per image
top5_prob, top5_catid = torch.topk(probabilities, 5)
for i in range(top5_prob.size(0)):
print(categories[top5_catid[i]], top5_prob[i].item())
模型描述
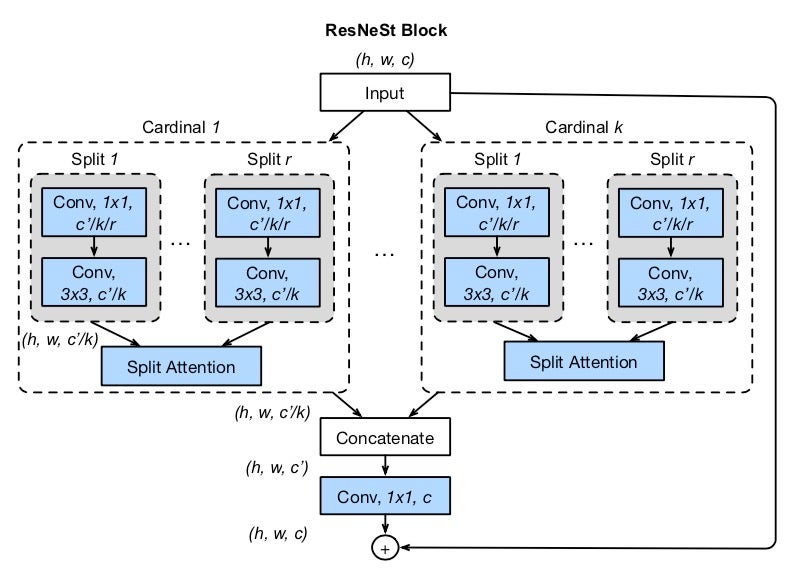
ResNeSt 模型来源于 ResNeSt: 分裂注意力网络 论文。
尽管图像分类模型在最近持续取得进展,但大多数下游应用(如目标检测和语义分割)仍采用 ResNet 变体作为骨干网络,因为它们结构简单且模块化。我们提出了一种简单而模块化的分裂注意力(Split-Attention)块,它实现了跨特征图组的注意力。通过像 ResNet 风格一样堆叠这些分裂注意力块,我们获得了一种新的 ResNet 变体,我们称之为 ResNeSt。我们的网络保留了 ResNet 的整体结构,以便直接用于下游任务,而不会引入额外的计算成本。ResNeSt 模型在相似模型复杂度的网络中表现出色,并且也有助于包括目标检测、实例分割和语义分割在内的下游任务。
| 裁剪尺寸 | PyTorch | |
|---|---|---|
| ResNeSt-50 | 224 | 81.03 |
| ResNeSt-101 | 256 | 82.83 |
| ResNeSt-200 | 320 | 83.84 |
| ResNeSt-269 | 416 | 84.54 |
参考文献