注意
单击 此处 下载完整的示例代码
带有 Emformer RNN-T 的设备 AV-ASR¶
作者: Pingchuan Ma、Moto Hira。
本教程演示了如何在流式设备输入(即笔记本电脑上的麦克风)上使用 TorchAudio 运行设备音频-视觉语音识别 (AV-ASR 或 AVSR)。AV-ASR 是从音频和视觉流中转录文本的任务,由于其对噪声的鲁棒性,近年来引起了很多研究关注。
注意
本教程需要 ffmpeg、sentencepiece、mediapipe、opencv-python 和 scikit-image 库。
安装 ffmpeg 库有多种方法。如果您使用的是 Anaconda Python 发行版,则 conda install -c conda-forge 'ffmpeg<7' 将安装兼容的 FFmpeg 库。
您可以运行 pip install sentencepiece mediapipe opencv-python scikit-image 来安装提到的其他库。
注意
要运行本教程,请确保您在 tutorial 文件夹中。
注意
我们在 Macbook Pro (M1 Pro) 上测试了 torchaudio 版本 2.0.2 上的教程。
import numpy as np
import sentencepiece as spm
import torch
import torchaudio
import torchvision
概述¶
实时 AV-ASR 系统如下所示,它由三个部分组成,一个数据收集模块、一个预处理模块和一个端到端模型。数据收集模块是硬件,例如麦克风和摄像头。它的作用是从现实世界收集信息。收集信息后,预处理模块会定位并裁剪面部。接下来,我们将原始音频流和预处理后的视频流馈送到我们的端到端模型以进行推理。
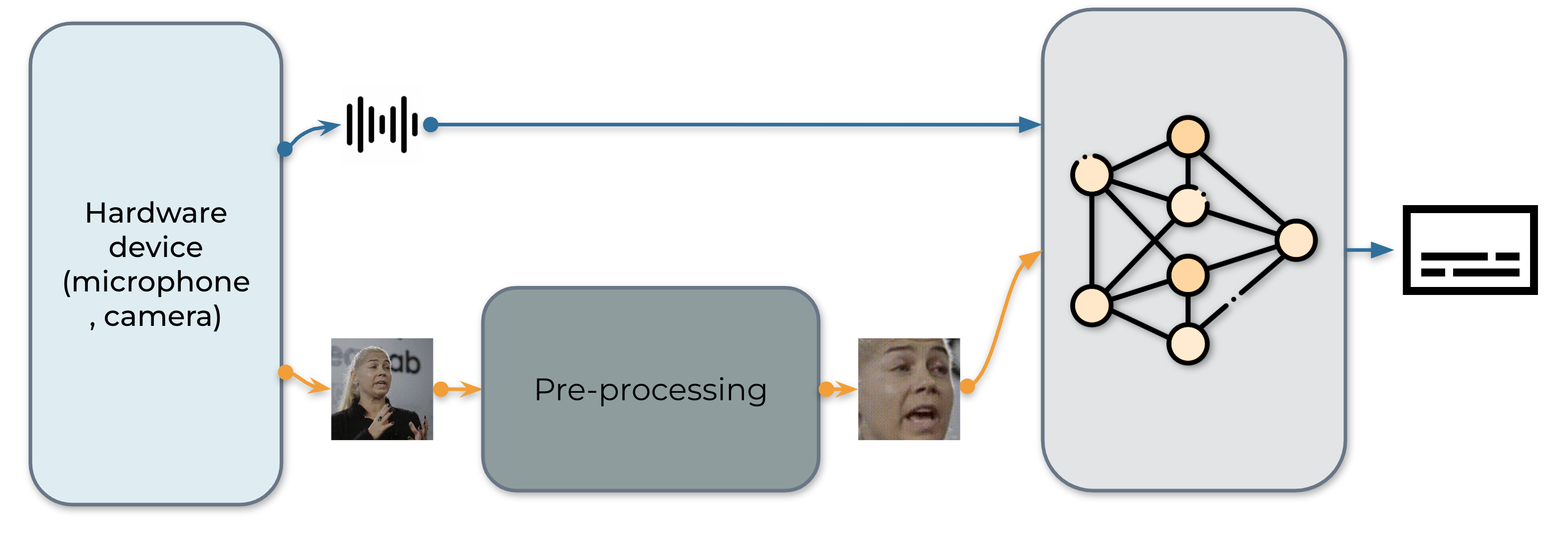
1. 数据采集¶
首先,我们定义一个函数来从麦克风和摄像头收集视频。具体来说,我们使用 StreamReader 类来进行数据收集,它支持从麦克风和摄像头捕获音频/视频。有关此类的详细用法,请参考 教程。
def stream(q, format, option, src, segment_length, sample_rate):
print("Building StreamReader...")
streamer = torchaudio.io.StreamReader(src=src, format=format, option=option)
streamer.add_basic_video_stream(frames_per_chunk=segment_length, buffer_chunk_size=500, width=600, height=340)
streamer.add_basic_audio_stream(frames_per_chunk=segment_length * 640, sample_rate=sample_rate)
print(streamer.get_src_stream_info(0))
print(streamer.get_src_stream_info(1))
print("Streaming...")
print()
for (chunk_v, chunk_a) in streamer.stream(timeout=-1, backoff=1.0):
q.put([chunk_v, chunk_a])
class ContextCacher:
def __init__(self, segment_length: int, context_length: int, rate_ratio: int):
self.segment_length = segment_length
self.context_length = context_length
self.context_length_v = context_length
self.context_length_a = context_length * rate_ratio
self.context_v = torch.zeros([self.context_length_v, 3, 340, 600])
self.context_a = torch.zeros([self.context_length_a, 1])
def __call__(self, chunk_v, chunk_a):
if chunk_v.size(0) < self.segment_length:
chunk_v = torch.nn.functional.pad(chunk_v, (0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, self.segment_length - chunk_v.size(0)))
if chunk_a.size(0) < self.segment_length * 640:
chunk_a = torch.nn.functional.pad(chunk_a, (0, 0, 0, self.segment_length * 640 - chunk_a.size(0)))
if self.context_length == 0:
return chunk_v.float(), chunk_a.float()
else:
chunk_with_context_v = torch.cat((self.context_v, chunk_v))
chunk_with_context_a = torch.cat((self.context_a, chunk_a))
self.context_v = chunk_v[-self.context_length_v :]
self.context_a = chunk_a[-self.context_length_a :]
return chunk_with_context_v.float(), chunk_with_context_a.float()
2. 预处理¶
在将原始流馈送到我们的模型之前,每个视频序列都必须经过特定的预处理过程。这涉及三个关键步骤。第一步是执行人脸检测。然后,对每个单独的帧进行对齐,使其与参考帧(通常称为平均面部)对齐,以规范化帧间的旋转和尺寸差异。预处理模块的最后一步是从对齐的面部图像中裁剪人脸区域。

|

|

|

|
|
|
|
|
import sys
sys.path.insert(0, "../../examples")
from avsr.data_prep.detectors.mediapipe.detector import LandmarksDetector
from avsr.data_prep.detectors.mediapipe.video_process import VideoProcess
class FunctionalModule(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self, functional):
super().__init__()
self.functional = functional
def forward(self, input):
return self.functional(input)
class Preprocessing(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.landmarks_detector = LandmarksDetector()
self.video_process = VideoProcess()
self.video_transform = torch.nn.Sequential(
FunctionalModule(
lambda n: [(lambda x: torchvision.transforms.functional.resize(x, 44, antialias=True))(i) for i in n]
),
FunctionalModule(lambda x: torch.stack(x)),
torchvision.transforms.Normalize(0.0, 255.0),
torchvision.transforms.Grayscale(),
torchvision.transforms.Normalize(0.421, 0.165),
)
def forward(self, audio, video):
video = video.permute(0, 2, 3, 1).cpu().numpy().astype(np.uint8)
landmarks = self.landmarks_detector(video)
video = self.video_process(video, landmarks)
video = torch.tensor(video).permute(0, 3, 1, 2).float()
video = self.video_transform(video)
audio = audio.mean(axis=-1, keepdim=True)
return audio, video
3. 构建推理管道¶
下一步是创建管道所需的部分。
我们使用基于卷积的前端从原始音频和视频流中提取特征。然后将这些特征通过两层 MLP 进行融合。对于我们的转导器模型,我们利用了 TorchAudio 库,它包含编码器 (Emformer)、预测器和联合网络。下面说明了所提出的 AV-ASR 模型的架构。
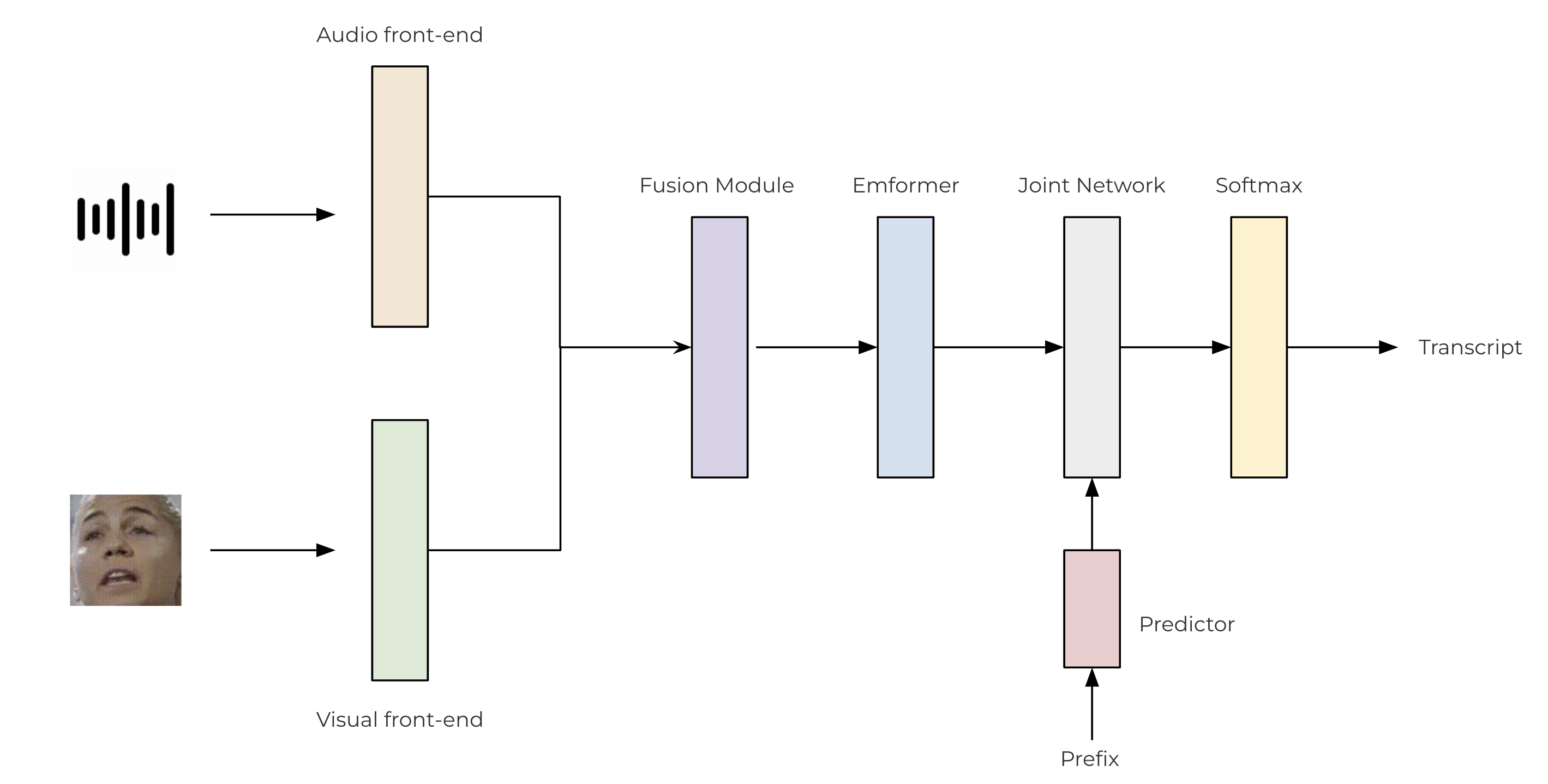
class SentencePieceTokenProcessor:
def __init__(self, sp_model):
self.sp_model = sp_model
self.post_process_remove_list = {
self.sp_model.unk_id(),
self.sp_model.eos_id(),
self.sp_model.pad_id(),
}
def __call__(self, tokens, lstrip: bool = True) -> str:
filtered_hypo_tokens = [
token_index for token_index in tokens[1:] if token_index not in self.post_process_remove_list
]
output_string = "".join(self.sp_model.id_to_piece(filtered_hypo_tokens)).replace("\u2581", " ")
if lstrip:
return output_string.lstrip()
else:
return output_string
class InferencePipeline(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self, preprocessor, model, decoder, token_processor):
super().__init__()
self.preprocessor = preprocessor
self.model = model
self.decoder = decoder
self.token_processor = token_processor
self.state = None
self.hypotheses = None
def forward(self, audio, video):
audio, video = self.preprocessor(audio, video)
feats = self.model(audio.unsqueeze(0), video.unsqueeze(0))
length = torch.tensor([feats.size(1)], device=audio.device)
self.hypotheses, self.state = self.decoder.infer(feats, length, 10, state=self.state, hypothesis=self.hypotheses)
transcript = self.token_processor(self.hypotheses[0][0], lstrip=False)
return transcript
def _get_inference_pipeline(model_path, spm_model_path):
model = torch.jit.load(model_path)
model.eval()
sp_model = spm.SentencePieceProcessor(model_file=spm_model_path)
token_processor = SentencePieceTokenProcessor(sp_model)
decoder = torchaudio.models.RNNTBeamSearch(model.model, sp_model.get_piece_size())
return InferencePipeline(
preprocessor=Preprocessing(),
model=model,
decoder=decoder,
token_processor=token_processor,
)
4. 主要过程¶
主要过程的执行流程如下
初始化推理管道。
启动数据采集子进程。
运行推理。
清理
from torchaudio.utils import download_asset
def main(device, src, option=None):
print("Building pipeline...")
model_path = download_asset("tutorial-assets/device_avsr_model.pt")
spm_model_path = download_asset("tutorial-assets/spm_unigram_1023.model")
pipeline = _get_inference_pipeline(model_path, spm_model_path)
BUFFER_SIZE = 32
segment_length = 8
context_length = 4
sample_rate = 19200
frame_rate = 30
rate_ratio = sample_rate // frame_rate
cacher = ContextCacher(BUFFER_SIZE, context_length, rate_ratio)
import torch.multiprocessing as mp
ctx = mp.get_context("spawn")
@torch.inference_mode()
def infer():
num_video_frames = 0
video_chunks = []
audio_chunks = []
while True:
chunk_v, chunk_a = q.get()
num_video_frames += chunk_a.size(0) // 640
video_chunks.append(chunk_v)
audio_chunks.append(chunk_a)
if num_video_frames < BUFFER_SIZE:
continue
video = torch.cat(video_chunks)
audio = torch.cat(audio_chunks)
video, audio = cacher(video, audio)
pipeline.state, pipeline.hypotheses = None, None
transcript = pipeline(audio, video.float())
print(transcript, end="", flush=True)
num_video_frames = 0
video_chunks = []
audio_chunks = []
q = ctx.Queue()
p = ctx.Process(target=stream, args=(q, device, option, src, segment_length, sample_rate))
p.start()
infer()
p.join()
if __name__ == "__main__":
main(
device="avfoundation",
src="0:1",
option={"framerate": "30", "pixel_format": "rgb24"},
)
Building pipeline...
Building StreamReader...
SourceVideoStream(media_type='video', codec='rawvideo', codec_long_name='raw video', format='uyvy422', bit_rate=0, num_frames=0, bits_per_sample=0, metadata={}, width=1552, height=1552, frame_rate=1000000.0)
SourceAudioStream(media_type='audio', codec='pcm_f32le', codec_long_name='PCM 32-bit floating point little-endian', format='flt', bit_rate=1536000, num_frames=0, bits_per_sample=0, metadata={}, sample_rate=48000.0, num_channels=1)
Streaming...
hello world
标签: torchaudio.io
脚本的总运行时间:(0 分钟 0.000 秒)



